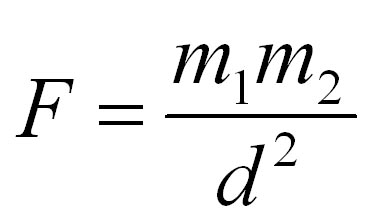Astronomy
Astronomy Powerpoint
Doppler Shift
Deep Space
(Any links or buttons in the powerpoint might not work)
Observations that need to be explained:
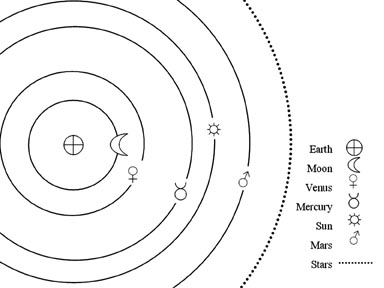
The Geocentric theory explains all of these phenomena. Since movement of the Earth cannot be felt early, scientists thought that the Earth was stationary and everything else moved around us. The geocentric theory says that the Earth is at the center of the solar system/ universe.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
But the Geocentric Theory does not explain this: Foucault Pendulum: The first good evidence of the earth's rotation was provided by a swinging pendulum. The pendulum would continue to swing in the same direction while the Earth rotated beneath it. A more recent source of evidence of rotation is the swirling pattern of weather systems seen by satellites. The Coriolis Effect makes the Foucault Pendulum work. The rotation of the Earth puts a "spin" on the air movement which causes a curve in the travel direction. In the Northern Hemisphere the turn is towards the object’s right. Galileo disproved the geocentric theory. He was the first to turn the telescope to the sky (he did not invent the telescope) for the purposes of Scientific observations. The moons of Jupiter orbit an object other than Earth. Galileo noticed that the four visible moons of Jupiter appeared to orbit around Jupiter and therefore did not revolve around the Earth. Galileo also observed the "phases of Venus" which demonstrated that Venus orbited around the sun.
The Heliocentric Theory explains all observations made from Earth. “Heliocentric” makes the sun the center of attention rather than the earth. Here's an article written by Benjamin Franklin about how much sense the Heliocentric Theory makes: The Whimsical Cook And here's a Powerpoint on the same Article. Rotation- to spin around an axis.
360°÷24hours= 15°/hr The Earth’s Rotation does not have the same speed all over
Revolution- to orbit around an object The Earth revolves around the sun in 365 ¼ days.
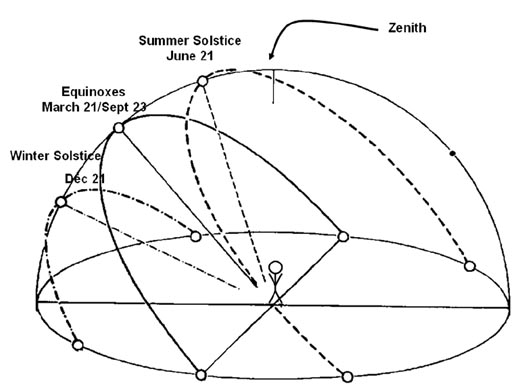
The Axis of Rotation is the imaginary line that the Earth turns about. The axis always points to the North Star. This is called Parallelism of the Earth's axis. The imaginary surface of the Earth's yearly trip around the sun is the Plane of Earth's Orbit. Warning! The following statement sounds crazy but you'll understand it if you read it slowly (or at least go back and re-read the last few lines)! "The axis is tilted by 23.5° from the perpendicular to the plane of its orbit."
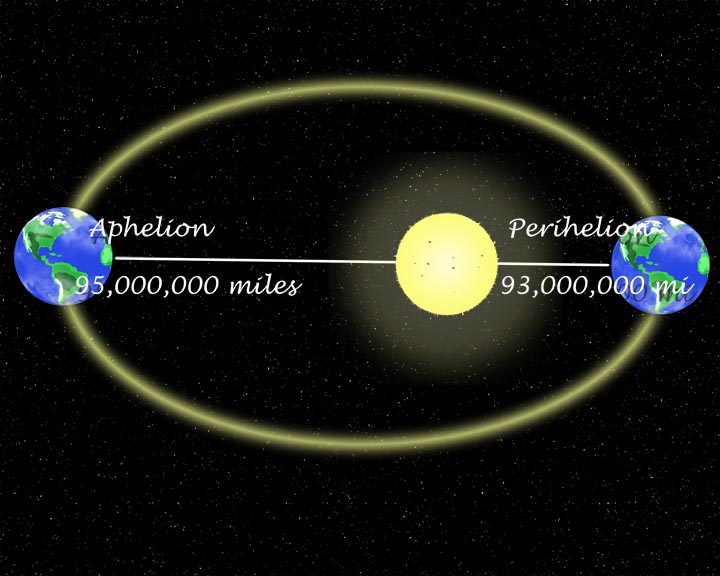
*Note: The seasons are NOT caused by the distance from the sun.
1) All planets travel in elliptical orbits with the sun at one focus. Note: The Earth's orbit is so close to a perfect circle that it can't be distinguished with the human eye. Here's a highly exagerated drawing of Earth's Elliptical orbit:
2) Each planet travels in such a way that a line joining the planet and the sun sweeps equal areas in equal times. Also called the law of equal areas. Each of the triangles in the diagram below will have the same area. Also, the time it takes for the planet to go from one position to the next will be equal (in this example a month).
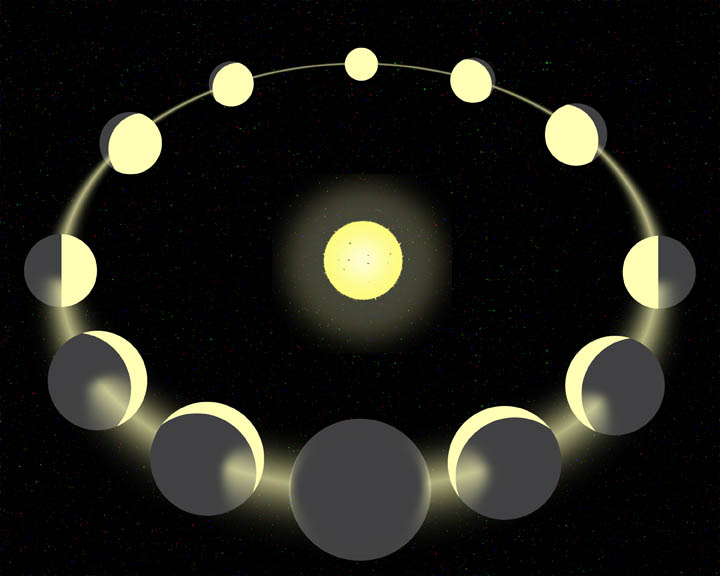
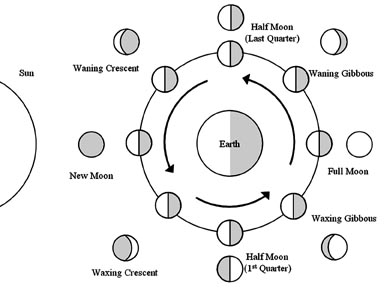
3) Keppler's Law of Harmonic Motion- Relationship between distance and period: P2 = D3 ("P squared = D cubed") Where P is the Period in Earth Years An “AU” is an astronomical unit, which is the average distance from the sun to the Earth. It is called the Law of Harmonic Motion because it describes how the planets move in harmony with each other- fastest in the center and gradually moving slower towards the outer solar system. The moon revolves around the Earth once a month (moonth). Moon rises 50 minutes later every day. It can be seen during the day just about as much as the night.
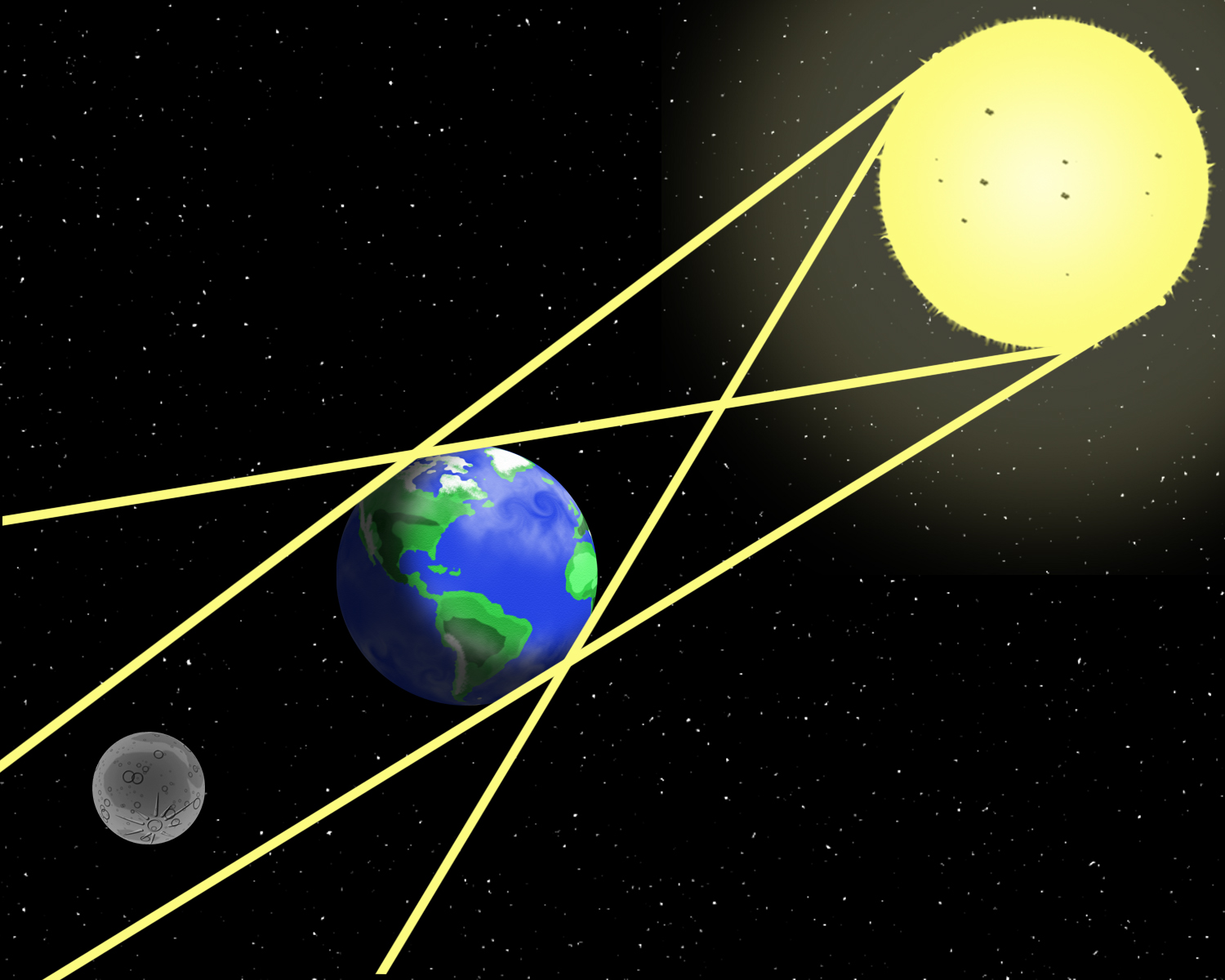
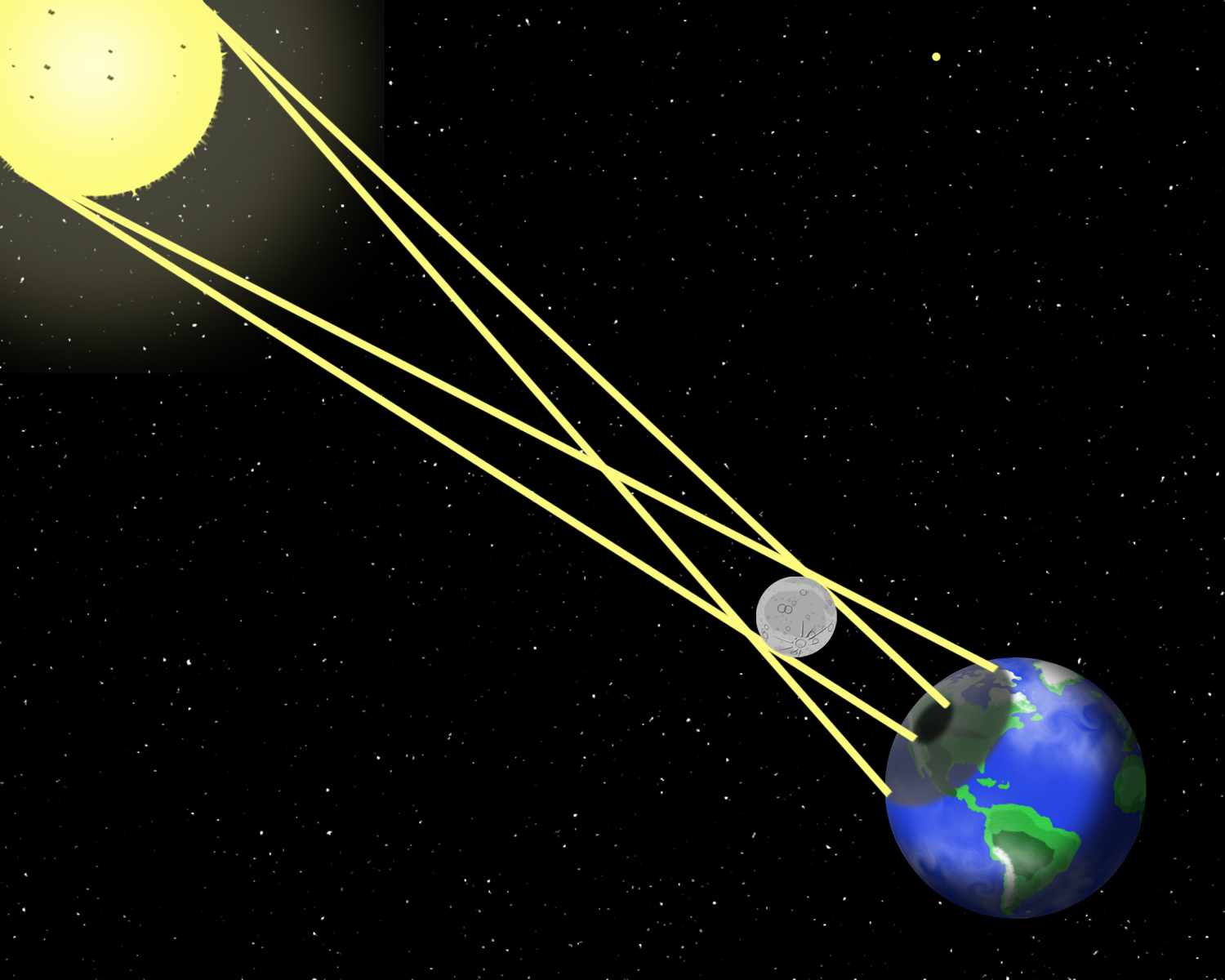
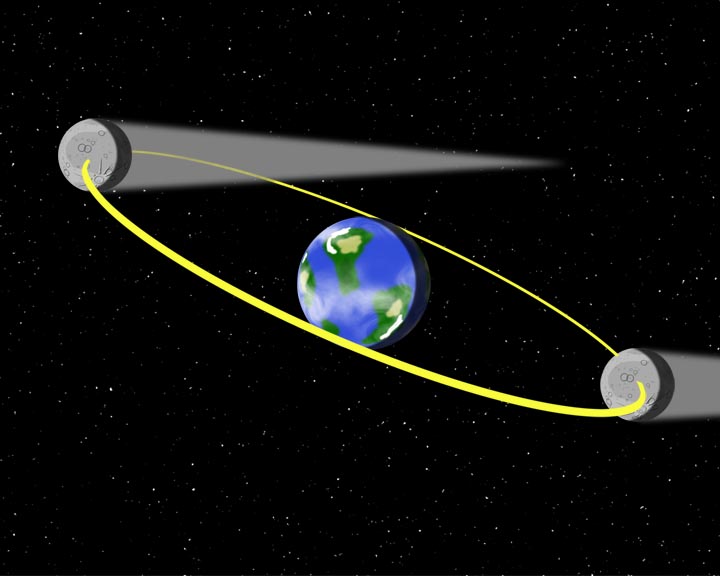
Eclipse means "gets dark." A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth blocks out the Moon's sunlight. The moon "gets dark" as it goes into the Earth's shadow. Lunar eclipses happen during a Full Moon.
A solar eclipse is when sun "gets dark" because the moon blocks sunlight from reaching the Earth. Solar Eclipses happen during a New Moon.
Eclipses do not occur every time there is a full or new moon because the moon's orbit around the Earth is inclined.
The strength of gravity depends on how close two objects are and their masses.
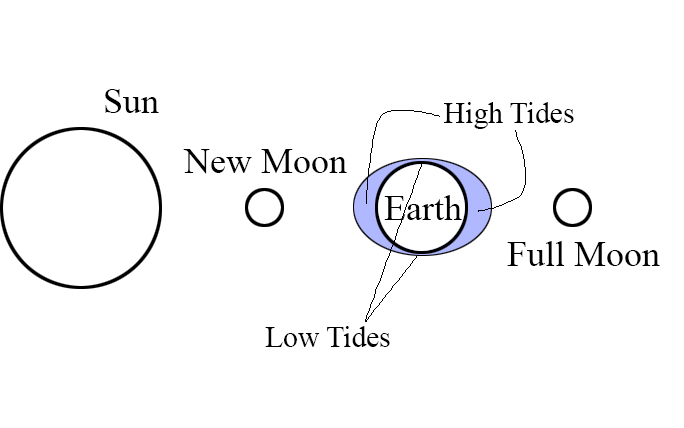
Where m1 and m2 are the masses of the objects and d is the distance between them. A Spring Tide is caused by a full moon and a new moon. The water “springs” from its highest level to its lowest for the month.
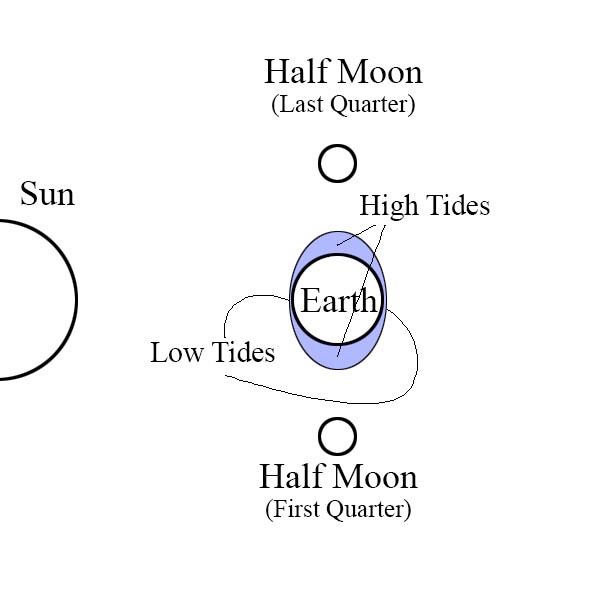
A Neap Tide is caused by the half moon phases. The high tide is not so high and the low is not so low.
Comets
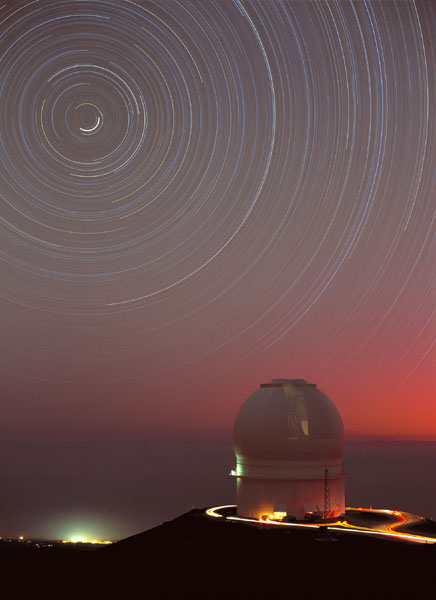
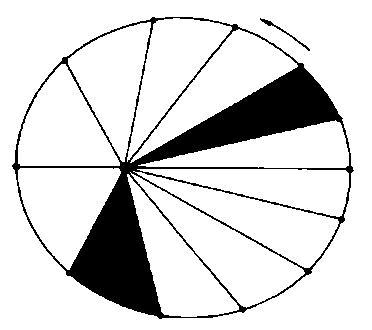
Meteor Showers result mainly from debris from the orbit of the comet. If the Earth crosses the path, the debris will fall to Earth as a visible meteor or “shooting star.” If the rock is big enough it will survive the fiery entry into the atmosphere and hit the surface as a meteorite. For more details on meteors and meteor showers Click Here. Circumpolar Stars As the Earth turns once a day, the stars appear to move across the sky in large arcs with the North Star at the middle of the arc. If a camera was left open for several hours. The stars will create streaks in the picture forming a bulls-eye around the North Star.
The stars that make a full circle without going below the horizon are called circumpolar stars and are part of circumpolar constellations. These stars are visible all night, every night of the year. In NY the Big Dipper is one of a few such circumpolar constellations. Stellar Fusion Stars get their energy by converting matter into energy. According to Einstein's famous equation (E=MC2) the amount of energy (E) equals the mass of the matter converted (M) times the speed of light squared (C2). As a result, a small amount of energy will give off a tremendous amount of energy. Stars are fueled by nuclear fusion which is a process of taking small atoms and fusing them together into larger atoms. During the process, some of the matter is converted into energy. The Life of a Star
The star is born and will continues to fuse its atoms until it runs out of fuel. At this point the star can go on two different paths depending on the size of the star:
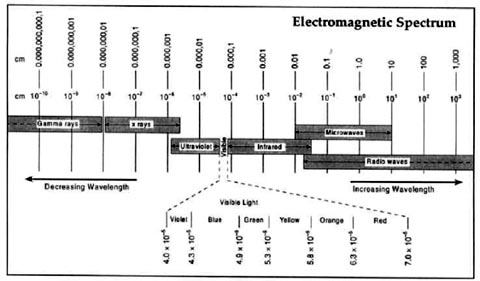
The Visible Spectrum- white light splits into the colors of the rainbow when passed through a prism. Red Orange Yellow Green Blue Indigo Violet ROY G. BIV There’s more to the spectrum than what you can see.
When an element is heated, it gives off light. As seen through a prism, the light will split into the basic colors that make that light (just like the rainbow). Each element has its own unique light with its own pattern of colors sometimes called the “fingerprint” of an element.
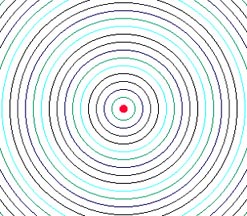
When sound is made by a stationary object, you hear a certain frequency. If you could see it, it would look like this...
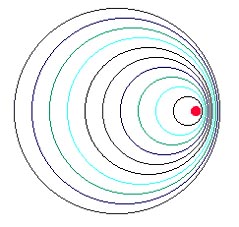
But when the sound moves towards you, it sounds higher in pitch and would look like this...
The faster the object moves, the higher the pitch. When the sound moves away, it sounds lower. The same shifting happens with the light from a moving star. When the star is moving closer the spectrum gets shifted to the blue end of the rainbow.
And when a star moves away from us...
Since the universe is expanding... The farther the object, the more extreme the red shift. Astronomers use this relationship between distance and speed to measure the distance to distant stars and galaxies. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||